Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
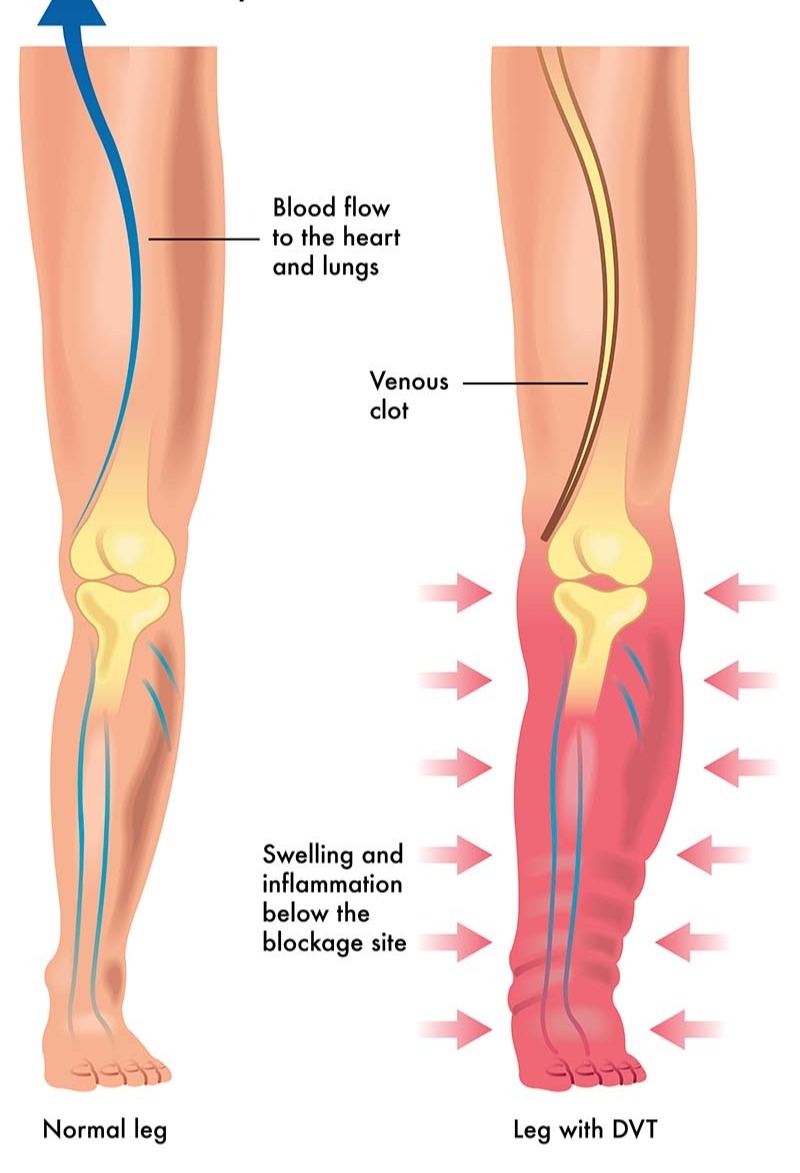
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when blood thickens in a clump to form a blood clot in the deep veins. Typically, the blood clots form in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis, but can also occur in the arm or shoulder. DVT’s can happen to anyone and may lead to serious illness, disability and in some cases death. Although DVT’s are underdiagnosed and serious, they are usually preventable and treatable if discovered early.
- Nearly 300,000 first-time cases of DVT occur in the U.S. every year, usually in the leg. (American Society for Vascular Surgery)
- About half of people with DVT have no symptoms at all. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
Signs and Symptoms
- Swelling
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Redness/warmth of the skin
- No symptoms at all
- Leg pain
Risk Factors
- Injury to a vein (fractures, severe muscle injury, major surgery)
- Slow blood flow (confined to bed, limited movement, sitting for long periods, paralysis)
- Increased estrogen (birth control, hormone replacement therapy, pregnancy- up to 3 months after giving birth)
- Surgery
- Certain chronic medical illnesses (heart/lung disease, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease- Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis)
- Previous DVT or pulmonary embolism or family history of either
- Age (risk increases as age increases)
- Obesity
- A catheter located in a central vein
- Inherited clotting disorders
- Cardiovascular disease
- Risk of thrombosis
Detection
If you are concerned by a swollen extremity, a comprehensive evaluation that includes an ultrasound must be completed to properly detect blockages or blood clots in deep veins. A blood test, MRI, CT scan or contrast venography may also be used to diagnose blood clots.
Treatment Options
- Blood thinners or anticoagulants prevent the blood clot from progressing or breaking off and traveling to other part of the body. Blood clots will naturally and slowly be absorbed by the body and further risk of clots developing is greatly reduced.
- In more severe cases, thrombolytics or “clot bustering drugs” may be used to dissolve the clot.
- In rare cases, a surgical procedure called a thrombectomy may be necessary to remove the clot.
Call To Schedule An Appointment
303-539-0736
Vascular Institute of the Rockies now offers ClotTriever® to remove Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT’S), an over-the-wire system designed to:
- Mechanically core clot from the vein wall
- Capture and remove large clot burden from big vessels
- Treat in a single session
- Eliminate the need for thrombolytics
- Eliminate ICU stay
Vascular Institute of the Rockies also now offers FlowTriever® to remove Pulmonary Embolisms (PE’s), an over-the-wire system designed to:
- Remove clot through both mechanical and aspiration mechanisms of action
- Capture and remove large clot burden from big vessels
- Treat in a single session
- Eliminate the need for thrombolytics
- Eliminate ICU stay
This advanced treatment for patients at the Vascular Institute of the Rockies aims to serve a large population suffering from DVT and PE, offering them effective solutions.